Эта статья началась с обсуждения на Stack Overflow: Why LINQ method Any does not check Count?. Здесь мы сравним производительность методов Any и Count != 0.
UPD: Вышла вторая часть статьи: Any() vs Count: часть 2, где сравниваются реализации в новых версиях .NET. Эта статья только о .NET 4.7.1.
Сначала добавим наш собственный метод-расширения, который реализует нужную логику сравнения:
public static class EnumerableExtensions
{
public static bool CustomAny<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source)
{
if (source == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(source));
}
if (source is ICollection<TSource> collection)
{
return collection.Count != 0;
}
using (var enumerator = source.GetEnumerator())
{
if (enumerator.MoveNext())
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
Идея: для коллекций, реализующих ICollection<T>, использовать свойство Count, чтобы избежать создания энумератора. Но будет ли это быстрее стандартного Any()?
Используем BenchmarkDotNet для тестирования.
Проверим на следующих коллекциях:
ListArrayHashSetDictionaryStackQueueSortedListSortedSet
Каждая коллекция содержит 1000 элементов. Сравниваем Any() и CustomAny():
[CategoriesColumn]
[GroupBenchmarksBy(BenchmarkLogicalGroupRule.ByCategory)]
public class SimpleCollections
{
[Params(1000)]
public int _size;
private List<int> _list;
private int[] _array;
private HashSet<int> _hashSet;
private Dictionary<int, int> _dictionary;
private Stack<int> _stack;
private Queue<int> _queue;
private SortedList<int, int> _sortedList;
private SortedSet<int> _sortedSet;
[GlobalSetup]
public void SetUp()
{
_list = new List<int>();
_array = new int[_size];
_hashSet = new HashSet<int>();
_dictionary = new Dictionary<int, int>();
_stack = new Stack<int>();
_queue = new Queue<int>();
_sortedList = new SortedList<int, int>();
_sortedSet = new SortedSet<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < _size; i++)
{
_list.Add(i);
_array[i] = i;
_hashSet.Add(i);
_dictionary[i] = i;
_stack.Push(i);
_queue.Enqueue(i);
_sortedList.Add(i, i);
_sortedSet.Add(i);
}
}
[Benchmark(Baseline = true, Description = "Any"), BenchmarkCategory("List")]
public bool ListAny()
{
return _list.Any();
}
[Benchmark(Description = "Custom"), BenchmarkCategory("List")]
public bool ListCount()
{
return _list.CustomAny();
}
///other collections
}
Первые результаты
BenchmarkDotNet=v0.10.14, OS=Windows 10.0.17134
Intel Core i7-2670QM CPU 2.20GHz (Sandy Bridge), 1 CPU, 8 logical and 4 physical cores
Frequency=2143565 Hz, Resolution=466.5126 ns, Timer=TSC
[Host] : .NET Framework 4.7.1 (CLR 4.0.30319.42000), 32bit LegacyJIT-v4.7.3110.0
DefaultJob : .NET Framework 4.7.1 (CLR 4.0.30319.42000), 32bit LegacyJIT-v4.7.3110.0
| Method | Categories | _size | Mean | Median | Scaled | ScaledSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any | List | 1000 | 38.88 ns | 38.32 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | List | 1000 | 16.49 ns | 16.50 ns | 0.43 | 0.02 |
| Any | Array | 1000 | 27.46 ns | 27.39 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | Array | 1000 | 51.21 ns | 50.60 ns | 1.87 | 0.05 |
| Any | HashSet | 1000 | 39.87 ns | 39.89 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | HashSet | 1000 | 15.06 ns | 15.01 ns | 0.38 | 0.00 |
| Any | Dictionary | 1000 | 51.14 ns | 50.83 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | Dictionary | 1000 | 17.41 ns | 17.36 ns | 0.34 | 0.01 |
| Any | Stack | 1000 | 42.10 ns | 42.29 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | Stack | 1000 | 49.41 ns | 48.60 ns | 1.17 | 0.06 |
| Any | Queue | 1000 | 44.68 ns | 44.41 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | Queue | 1000 | 50.68 ns | 50.66 ns | 1.14 | 0.04 |
| Any | SortedList | 1000 | 42.89 ns | 42.55 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | SortedList | 1000 | 17.48 ns | 17.17 ns | 0.41 | 0.02 |
| Any | SortedSet | 1000 | 220.19 ns | 219.66 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | SortedSet | 1000 | 18.46 ns | 18.34 ns | 0.08 | 0.00 |
Здесь и далее испльзуется легенда:
Categories : Collection type
_size : Number of elements in collection
Mean : Arithmetic mean of all measurements
Error : Half of 99.9% confidence interval
StdDev : Standard deviation of all measurements
Median : Value separating the higher half of all measurements (50th percentile)
Scaled : Mean(CurrentBenchmark) / Mean(BaselineBenchmark)
ScaledSD : Standard deviation of ratio of distribution of [CurrentBenchmark] and [BaselineBenchmark]
1 ns : 1 Nanosecond (0.000000001 sec)
Как мы видим, новый метод с проверкой Count быстрее или сравним по производительности со стандартным Any() за исключением нескольких коллекций.
Почему массив замедлился?
Хотя массивы реализуют ICollection<T>, проверка типа source is ICollection<T> в .NET работает медленнее для них. Решение — добавить отдельную проверку на массив:
public static class EnumerableExtensions
{
public static bool CustomAny<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source)
{
// ... остальная логика ...
if (source is TSource[] array)
{
return array.Length != 0;
}
// ... остальная логика ...
}
}
После доработки результаты для массива улучшились:
| Method | Categories | _size | Mean | Scaled | ScaledSD | ScaledSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any | Array | 1000 | 27.11 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | Array | 1000 | 18.87 ns | 0.70 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
Stack and Queue
Проблема: Stack<T> и Queue<T> не реализуют ICollection<T>:
public class Stack<T> : IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable, ICollection, IReadOnlyCollection<T>
public class Queue<T> : IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable, ICollection, IReadOnlyCollection<T>
Но имеют необобщенный ICollection. Добавим проверку:
public static class EnumerableExtensions
{
public static bool CustomAny<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source)
{
// ... остальная логика ...
if (source is ICollection baseCollection)
{
return baseCollection.Count != 0;
}
// ... остальная логика ...
return false;
}
}
Результаты после оптимизации:
| Method | Categories | _size | Mean | Scaled | ScaledSD | ScaledSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any | Stack | 1000 | 39.56 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | Stack | 1000 | 31.66 ns | 0.80 | 0.01 | 0.06 |
| Any | Queue | 1000 | 42.90 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | Queue | 1000 | 31.69 ns | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.04 |
Загадка SortedSet
Почему Any() для SortedSet такой медленный? Всё дело в реализации его энумератора.
Метод GetEnumerator создаёт структуру типа Enumerator, которая принимает SortedSet<T> в качестве параметра конструктора:
internal Enumerator(SortedSet<T> set)
{
this.tree = set;
this.tree.VersionCheck();
this.version = this.tree.version;
this.stack = new Stack<SortedSet<T>.Node>(2 * SortedSet<T>.log2(set.Count + 1));
this.current = (SortedSet<T>.Node) null;
this.reverse = false;
this.siInfo = (SerializationInfo) null;
this.Intialize();
}
Взглянем на метод Intialize (с опечаткой в названии):
private void Intialize()
{
this.current = (SortedSet<T>.Node) null;
SortedSet<T>.Node node1 = this.tree.root;
while (node1 != null)
{
SortedSet<T>.Node node2 = this.reverse ? node1.Right : node1.Left;
SortedSet<T>.Node node3 = this.reverse ? node1.Left : node1.Right;
if (this.tree.IsWithinRange(node1.Item))
{
this.stack.Push(node1);
node1 = node2;
}
else
node1 = node2 == null || !this.tree.IsWithinRange(node2.Item) ? node3 : node2;
}
}
Класс SortedSet<T> построен на бинарном дереве, а метод Intialize обходит все узлы дерева и помещает элементы в стек.
Таким образом, при создании энумератора для SortedSet, его внутренняя реализация фактически формирует новую коллекцию со всеми элементами.
Чем больше элементов, тем больше времени тратится на это копирование:
| Method | _size | Mean | Scaled |
|---|---|---|---|
| Any | 1000 | 230.64 ns | 1.00 |
| Custom | 1000 | 22.23 ns | 0.10 |
| Any | 10000 | 288.27 ns | 1.00 |
| Custom | 10000 | 21.72 ns | 0.08 |
| Any | 100000 | 343.54 ns | 1.00 |
| Custom | 100000 | 21.70 ns | 0.06 |
Мы проверили наиболее популярные коллекции и можно сказать, что мы должны использовать свойство Count вместо вызова метода Enumerable.Any().
Но всегда ли безопасно использовать Count?
Есть ли коллекции, где вычисление свойства Count занимает больше времени, чем создание энумератора? Вы будете удивлены.
Concurrent collections
Все коллекции до этого были не потокобезопасными - они не могут быть использованы в многопоточном коде без дополнительных синхронизаций. Чтобы этого избежать, был создан отдельный набор потокобезопасных коллекций.
ConcurrentBagConcurrentDictionaryConcurrentQueueConcurrentStack
Давайте для теста заполним эти коллекции из разных потоков симулируя многопоточную работу:
[GlobalSetup]
public void SetUp()
{
_bag = new ConcurrentBag<int>();
_dictionary = new ConcurrentDictionary<int, int>();
_queue = new ConcurrentQueue<int>();
_stack = new ConcurrentStack<int>();
var tasksCount = 10;
var batch = _size / tasksCount;
var tasks = new Task[tasksCount];
for (int i = 0; i < tasksCount; i++)
{
var task = i;
tasks[task] = Task.Run(() =>
{
var from = task * batch;
var to = (task + 1) * batch;
for (int j = from; j < to; j++)
{
_bag.Add(j);
_dictionary[j] = j;
_queue.Enqueue(j);
_stack.Push(j);
}
});
}
Task.WaitAll(tasks);
}
Результаты
| Method | Categories | _size | Mean | Scaled | ScaledSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any | ConcurrentBag | 1000 | 7,065.75 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | ConcurrentBag | 1000 | 267.89 ns | 0.04 | 0.00 |
| Any | ConcurrentDictionary | 1000 | 39.29 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | ConcurrentDictionary | 1000 | 6,319.42 ns | 160.88 | 2.45 |
| Any | ConcurrentStack | 1000 | 28.08 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | ConcurrentStack | 1000 | 3,179.18 ns | 113.23 | 0.93 |
| Any | ConcurrentQueue | 1000 | 72.12 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | ConcurrentQueue | 1000 | 48.28 ns | 0.67 | 0.02 |
Получили неожиданные результаты. Где-то Any() очень медленный, а где-то наоборот.
ConcurrentBag
Метод GetEnumerator работает аналогично как и в SortedSet. Он блокирует исходную коллекцию и копирует все элементы в новый список:
private List<T> ToList()
{
List<T> objList = new List<T>();
for (ConcurrentBag<T>.ThreadLocalList threadLocalList = this.m_headList; threadLocalList != null; threadLocalList = threadLocalList.m_nextList)
{
for (ConcurrentBag<T>.Node node = threadLocalList.m_head; node != null; node = node.m_next)
objList.Add(node.m_value);
}
return objList;
}
Свойство Count блокирует коллекцию и суммирует внутренние счетчики количества элементов:
private int GetCountInternal()
{
int num = 0;
for (ConcurrentBag<T>.ThreadLocalList threadLocalList = this.m_headList; threadLocalList != null; threadLocalList = threadLocalList.m_nextList)
checked { num += threadLocalList.Count; }
return num;
}
Поэтому, Count намного быстрее метода Any().
ConcurrentDictionary
GetEnumerator не создаёт новой коллекции, а использует ключевое слово yield для ленивой итерации по коллекции, поэтому Any() совершает всего одну итерацию:
public IEnumerator<KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>> GetEnumerator()
{
foreach (ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>.Node bucket in this.m_tables.m_buckets)
{
ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>.Node current;
for (current = Volatile.Read<ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>.Node>(ref bucket); current != null; current = current.m_next)
yield return new KeyValuePair<TKey, TValue>(current.m_key, current.m_value);
current = (ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>.Node) null;
}
}
Свойство Count блокирует коллекцию и подсчитывает количество элементов:
public int Count
{
[__DynamicallyInvokable] get
{
int locksAcquired = 0;
try
{
this.AcquireAllLocks(ref locksAcquired);
return this.GetCountInternal();
}
finally
{
this.ReleaseLocks(0, locksAcquired);
}
}
}
private int GetCountInternal()
{
int num = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < this.m_tables.m_countPerLock.Length; ++index)
num += this.m_tables.m_countPerLock[index];
return num;
}
И чем больше элементов в коллекции, тем больше времени требуется на подсчет:
| Method | _size | Mean | Scaled | ScaledSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any | 10 | 37.79 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | 10 | 239.63 ns | 6.34 | 0.18 |
| Any | 100 | 34.46 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | 100 | 823.62 ns | 23.90 | 0.58 |
| Any | 1000 | 38.22 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | 1000 | 6,264.17 ns | 163.92 | 2.09 |
| Any | 10000 | 35.57 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Custom | 10000 | 24,819.31 ns | 697.82 | 11.97 |
Профайлер показывает, что больше всего времени теряется на блокировках:
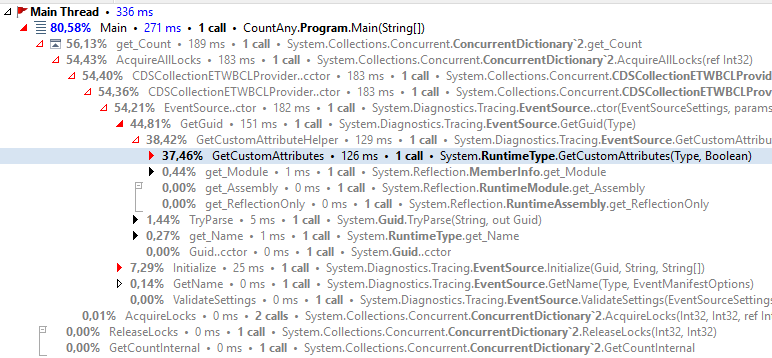
ConcurrentStack
GetEnumerator использует ленивое перечисление элементов, поэтому вызов Any() дешев:
private IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator(ConcurrentStack<T>.Node head)
{
for (ConcurrentStack<T>.Node current = head; current != null; current = current.m_next)
yield return current.m_value;
}
В то время как Count просто подсчитывает количество элементов даже без блокировки:
public int Count
{
[__DynamicallyInvokable] get
{
int num = 0;
for (ConcurrentStack<T>.Node node = this.m_head; node != null; node = node.m_next)
++num;
return num;
}
}
ConcurrentQueue
Реализация GetEnumerator несколько сложна, но внутри используется ленивое перечисление. Count использует простые арифметические операции без блокировки. Можем использовать оба способа.
Как можно заметить, потокобезопасные коллекции имеют более сложную реализацию и отличаются от своих классических коллег.
Универсальный метод для всех коллекций?
В классическом фреймворке (.NET 4.7.1) мы должны использовать Count или Any() в зависимости от коллекции.
В новых версиях .NET ситуация изменилась, вы можете ознакомиться с актуальным исследованием в статье Any() vs Count: часть 2.